Instructions
Study the first 3 graphics and then answer the questions that follow each. Once you are sure you understand how the lunar
day, the position of the sun and the moon, and orbital variations affect the tides, then try to apply this knowledge, and
Be the Captain.
Introduction
Knowing when and how much the tides will rise and fall each day is important to beachcombers, mariners, fishermen, and the
people who operate seaside industrial and commercial facilities. Miscalculating the arrival and size of the tides can have
expensive, even deadly, consequences.
Predicting the tides is complicated because the tides are affected by many factors. In this activity, you’ll have a chance
to consider some of the most important and universal influences, those due to the movements of the sun, the moon, and the
earth. In reality, a number of local and transient factors, such as the shape of the coastline, the flow of currents, and
the weather, must also be taken into account.
Instructions
Study the image to see how the distances between the Earth and the moon and sun change over the course of a month and a
year, then answer the questions below.
Orbital Shape
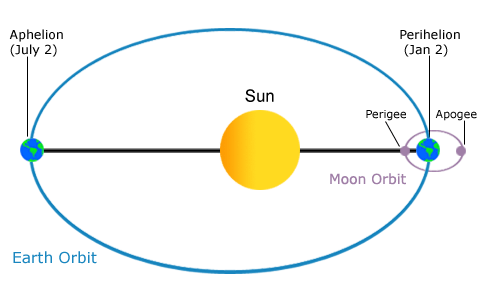
The orbital paths of the moon around the earth and the earth around the sun are both elliptical. The point in the moon’s
orbit where it is farthest from the earth is called apogee, while it’s closest approach is known as perigee. Earth is at
its maximum distance from the sun at aphelion, and at its minimum distance at perihelion. These orbits produce cyclical
changes in the height of the tides.




