
By J.M. Adovasio, Expedition Principal Investigator - Mercyhurst University
and C. Andrew Hemmings, Expedition Principal Investigator - Mercyhurst University
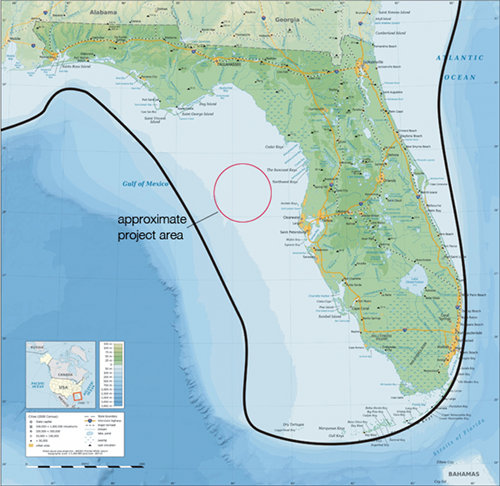
A modern map of Florida shows (with a dark line) the approximate location of the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM) coastline. Image courtesy of Exploring the Submerged New World 2012 Expedition, NOAA-OER. Download image (jpg, 69 KB).
The maximum amount of water trapped in glacial ice occurred roughly 26,000 years ago. This point in time is referred to as the Last Glacial Maximum (LGM). At the time of the LGM, the Earth’s ocean levels were at their lowest point and extensive reaches of dry land were exposed along the continents’ coasts. As the glaciers began to melt, sea level rose worldwide, resulting in nearly a 10% reduction of the Earth’s entire landmass. In the Northeastern Gulf of Mexico, this translates to the inundation (covering with water) of more than 350,000 km2 of what had been dry land, which in turn forced the relocation of plants, animals, and — what is of primary interest to our research — people.
Compared to today, LGM Florida encompassed twice its present land area and was probably slightly cooler and dryer. Furthermore, Florida’s Pleistocene landscape was not as extensively traversed by rivers as it is today. Instead, groundwater was much deeper in the rock and closer to the coasts, as it ran to its lowest level. Typically the greatest amount of surficial fresh water is within 10km of the ocean coastline.
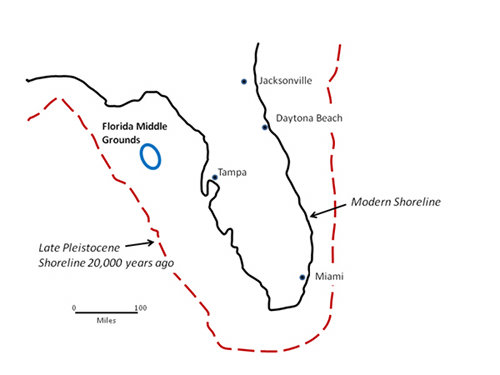
A simplified version of the above map. During the Late Pleistocene, Florida's shoreline extended much farther offshore than the present coast. The Florida Middle Grounds were part of the exposed coastal margin. Image courtesy of Exploring the Submerged New World 2012 Expedition, NOAA-OER. Download image (jpg, 20 KB).
It took over 20,000 years for the sea to transition from the LGM shoreline up to the modern coast of Florida. As ocean water covered the ancient landscape from about 26,000 to 5,000 years ago, several distinct and profound changes occurred simultaneously: the landmass of Florida became greatly reduced with significant changes to the contours of the state’s coastlines; the surficial water aquifer and deeper Floridian aquifer became elevated; weather patterns changed; and biotic (i.e., plant and animal) communities rearranged themselves on the landscape, with some species flourishing, others staying the same, and several (like the mastodon) becoming extinct.
Generally speaking, the transition to present-day Florida witnessed an increase in the number of springs and rivers, the climate became somewhat warmer and wetter, greater numbers of trees flourished on the landscape, species that had once been widely dispersed instead became concentrated in favored areas for survival, and some animals became extinct.
An important consequence of these changes for early human populations was that food and fresh water were no longer available in the same places from generation to generation, although on a yearly basis the conditions for human life were still relatively stable, if probably somewhat less so than today.
Understanding the nature of these changes also has important consequences for how we conduct our research. Because Pleistocene peoples relied heavily on the availability of fresh water, plants and animals for food, and high-quality lithic (stone or rock) material for the production of stone tools, our knowledge of these important parameters permits the selection of specific high-probability areas for investigation. Hence, by positing what would have been the most attractive sites on the Pleistocene landscape — such as the concentrated and species-rich environments just inside the incoming coastline — we increase the likelihood for site discovery and understanding the Pleistocene lifeway of the earliest Floridians.
A nuanced understanding of long-term climate and environmental change, from the end of the Pleistocene through the Holocene, is critical to seeing what the “old” Floridian land mass was like at any given moment in time, and how plants, animals, and people were able to live as their world changed around them. Our recent work surveying and diving portions of this drowned landscape when coupled with sea level rise curves and reconstruction models indicate that more than 90% of the LGM landscape was still dry land by the time we know people had blanketed the southeast with sites at the end of the Pleistocene. The need for available fresh water and the proximity to marine resources from the ocean suggests places with water near the coast would have been very desirable campsites to people during the Pleistocene. The enduring human need for food and water helps direct our efforts to find where exactly people might have lived thousands of years ago.
At each of these sites we hope to locate prehistoric human made artifacts, bones of Pleistocene animals, such as the mastodon or mammoth, and perhaps datable organic material such as pieces of wood. Any such finds would indicate that the now inundated Pleistocene landscape of Florida in the Gulf of Mexico is still preserved, accessible to archaeologists, and contains prehistoric evidence of the use of this landscape by people and animals alive at the end of the last Ice Age.